上海优宁维生物科技股份有限公司代理商
19 年
手机商铺
商家活跃:
产品热度:
- NaN
- 0
- 0
- 2
- 2
公司新闻/正文
BioXcell特色产品推荐之:InVivoMAb anti-mouse OX40 (CD134)
360 人阅读发布时间:2022-04-18 15:04
一 产品介绍
OX-40在活化的CD4和CD8 T细胞上表达,但在静止的幼稚T细胞或大多数静止的记忆T细胞上没有发现。尽管最初认为OX-40的表达仅限于活化的常规T细胞,但现在已经在活化的调节性T细胞、NKT细胞、NK细胞和嗜中性粒细胞上观察到了。OX-40在调节CD4和CD8 T细胞克隆扩增中起主要作用。它向抗原反应性幼稚T细胞提供共刺激信号以延长增殖,并增加几种细胞因子的产生。这由OX-40敲除小鼠证明,其在免疫后产生较少的初级效应CD4 T细胞。此外,用OX-40的激动剂抗体进行的体内治疗已经显示出强烈地增强了抗原特异性效应T细胞的产生,并防止了T细胞耐受性的诱导。OX-86抗体是一种激动性抗体,已被证明能延缓体内肿瘤的生长。
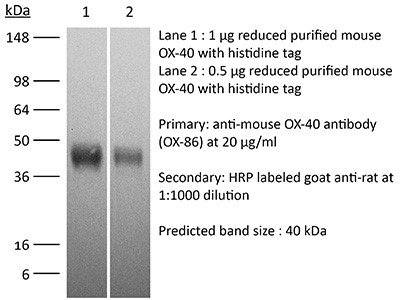
二 产品详情
| 产品编号 | BE0031 |
| 抗体亚型 | Rat IgG1, κ |
| 推荐同型对照 | InVivoMAb rat IgG1 isotype control, anti-horseradish peroxidase |
| 推荐稀释buffer | InVivoPure™ pH 7.0 Dilution Buffer |
| 免疫原 | Recombinant mouse OX40-CD4 chimeric protein |
| 用途 | in vivo OX40 activation in vitro OX40 activation Western blot |
| 产品形式 | PBS, pH 7.0 |
| 内毒素测定 | <2EU/mg (<0.002EU/μg) Determined by LAL gel clotting assay |
| 纯度 | >95% Determined by SDS-PAGE |
| 无菌处理 | 0.2 μM filtered |
| 生产形式 | Purified from tissue culture supernatant in an animal free facility |
| 纯化形式 | Protein G |
| 分子量 | 150 kDa |
| 保存条件 | The antibody solution should be stored at the stock concentration at 4°C. Do not freeze. |
三 已发表文献
| 用途 | 已发表文献 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Bartkowiak, T., et al. (2015). “Unique potential of 4-1BB agonist antibody to promote durable regression of HPV+ tumors when combined with an E6/E7 peptide vaccine.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(38): E5290-5299. |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Makkouk, A., et al. (2015). “Three steps to breaking immune tolerance to lymphoma: a microparticle approach.” Cancer Immunol Res 3(4): 389-398 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Zander, R. A., et al. (2015). “PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity.” Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Guo, Z., et al. (2014). “PD-1 blockade and OX40 triggering synergistically protects against tumor growth in a murine model of ovarian cancer.” PLoS One 9(2): e89350. |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Krupnick, A. S., et al. (2014). “Central memory CD8+ T lymphocytes mediate lung allograft acceptance.” J Clin Invest 124(3): 1130-1143 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Redmond, W. L., et al. (2014). “Combined targeting of costimulatory (OX40) and coinhibitory (CTLA-4) pathways elicits potent effector T cells capable of driving robust antitumor immunity.” Cancer Immunol Res 2(2): 142-153 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Hu, Z., et al. (2013). “Regulatory CD8+ T cells associated with erosion of immune surveillance in persistent virus infection suppress in vitro and have a reversible proliferative defect.” J Immunol 191(1): 312-322. |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Kurche, J. S., et al. (2012). “Type I IFN-dependent T cell activation is mediated by IFN-dependent dendritic cell OX40 ligand expression and is independent of T cell IFNR expression.” J Immunol 188(2): 585-593 |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Xiao, X., et al. (2012). “New insights on OX40 in the control of T cell immunity and immune tolerance in vivo.” J Immunol 188(2): 892-901. |
| in vivo OX40 activation | Murray, S. E., et al. (2011). “NF-kappaB-inducing kinase plays an essential T cell-intrinsic role in graft-versus-host disease and lethal autoimmunity in mice.” J Clin Invest 121(12): 4775-4786 |
详情请咨询 BioXcell 中国授权代理-优宁维生物
上海优宁维生物科技股份有限公司
试剂 | 耗材 | 仪器 | 软件 | 定制 | 实验服务 | 供应链
免费热线:4008-168-068
咨询邮箱:info@univ-bio.com
订购商城:www.univ-bio.com
微信公众平台:优宁维抗体专家,欢迎关注!
小优博士(小程序):5大课堂, 让你的科研不再难!